The professional landscape is undergoing unprecedented change. Technological advancements, globalization and evolving industry needs are shifting workforce development strategies. Given that job requirements are now in constant flux, the traditional concept of upskilling has become a popular strategy. However, the question to answer is, “Will this be sufficient in the long run?”
The modern professional landscape demands a broader, more integrated approach—one that goes beyond acquiring specific skills to embrace a comprehensive model of professional development. This article explores the shift from upskilling to holistic professional development, highlighting strategies, challenges and implications for both individuals and organizations from a learning perspective.
Understanding the shift
Upskilling plays a crucial role in keeping pace with rapid change by focusing on acquiring targeted technical skills. Online learning platforms, micro-credentials and short-term training programs have made upskilling accessible and efficient. However, upskilling has limitations as it often focuses on a narrow set of skills without addressing the broader context of professional growth. This can lead to a workforce that is technically proficient but lacks the critical thinking, problem-solving and adaptability needed to thrive in the long run.
The shift toward comprehensive development
Comprehensive professional development takes a more holistic view, focusing not just on skills but also on knowledge, attitudes and behaviors. It aims to create well-rounded professionals who can not only perform specific tasks but also analyze situations, make sound decisions and navigate complex challenges.
This approach incorporates human (soft) skills development, leadership training, strategic thinking, innovation, emotional intelligence and life-long learning. These skills encourage employees to think strategically about the organization’s goals and identify innovative solutions fostering a culture of continuous improvement. According to the Future of Work research, analytical thinking and creative thinking remain the most important skills for workers in 2023.
Key strategies for transition
Personalized learning pathways: Personalized learning is central to professional development. Recent research emphasizes the importance of personalized learning in professional development. Tailoring learning experiences to individual needs, interests and career goals ensures that they remain relevant and engaging. This can be achieved through personalized training programs, adaptive learning technologies, mentorship and coaching opportunities.
In a single year, helping employees develop their careers climbed from No. 9 on L&D’s priority list to No. 4. — LinkedIn Workplace Learning Report (2024)
Continuous feedback loop: Regular feedback is crucial for continuous improvement. According to a 2024 study by the Work Institute, employees who receive regular feedback are more engaged and productive. Integrating real-time feedback loops into the learning process helps individuals understand their progress, identify areas for improvement and make necessary adjustments. This can be facilitated through performance reviews, peer evaluations and self-assessment tools.
Over 40 percent of the reasons for leaving are different when the exit interview is completed after the employee has departed. A best practice is for employees to understand expectations of them to provide feedback throughout their employment.— 2024 Retention Report, Work Institute
Experiential learning opportunities: Experiential learning creates a memorable and engaging environment in which participants can pursue the development of new competencies. Research by ATD indicated in 2022 that experiential learning experiences, such as case studies and role-playing, feedback, coaching and mentorship programs, action learning projects, are invaluable. These opportunities allow individuals to apply theoretical knowledge in practical settings, fostering deeper understanding and skill retention.
Challenges in transition
The shift from upskilling to holistic professional development is not without challenges. One major challenge is balancing the need for immediate skill acquisition with long-term developmental goals. This requires a strategic approach to integrate short-term and long-term learning objectives.
Organizations must also address varying learning preferences and styles, ensuring that all employees have access to meaningful learning opportunities.
Another challenge is aligning professional development initiatives with organizational objectives. Ensuring that individual growth contributes to the overall success of the organization requires strategic planning and integration of development programs into the corporate culture.

Implications for learning outcomes
The implications of this transition are significant and far-reaching:
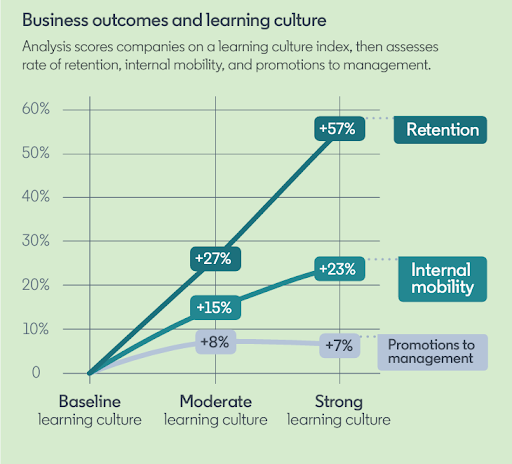
Source: LinkedIn Learning (2024), “Workplace Learning Report 2024.”
For individuals:
- Growth mindset: Professional development fosters a growth mindset, encouraging continuous improvement and learning.
- Resilience and adaptability: Individuals become more resilient and adaptable, equipped to handle the uncertainties of the modern job market.
- Lifelong learning: Embracing a culture of lifelong learning ensures sustained personal and professional growth.
For organizations:
- Agility and innovation: A workforce engaged in continuous learning is more agile and capable of driving innovation.
- Employee engagement and retention: Employees who see opportunities for growth and development are more likely to be engaged and loyal to the organization. Ninety percent of organizations are concerned about employee retention and providing learning opportunities is the number one retention strategy.
- Enhanced competitiveness: Organizations with a well-developed, skilled workforce are better positioned to compete in a dynamic market.
Enhancing organizational learning with AI
Artificial intelligence is rapidly transforming various facets of organizational operations, and one of the most significant areas of impact is learning and development.
One of the most prominent benefits of AI in organizational learning is its ability to personalize training content based on the skills to be developed for an aspirational role. AI’s ability to analyze large datasets allows it to identify current skills gaps and predict future learning needs. AI’s role in predictive analytics, involving examining employee performance data to identify areas where skills are lacking is crucial for organizations aiming to stay ahead in a rapidly changing job market.
By understanding where skills gaps exist, organizations can develop targeted training programs to address these deficiencies. Furthermore, AI can forecast future skill requirements based on industry trends and organizational goals, which can then be mapped to the skills deficiency in the organization.
Experiential learning, where employees learn by doing, is significantly enhanced by AI technologies. The IBM Watson Training explores AI’s capability to create immersive learning experiences through virtual reality and augmented reality. These technologies provide realistic, interactive environments where employees can practice and refine their skills without real-world consequences.
For instance, VR simulations can be used for training in complex and high-risk environments such as health care, manufacturing and aviation. These simulations allow employees to gain hands-on experience and develop their skills in a safe, controlled setting. It has become very normal to use simulation platforms that use AI and virtual reality to provide surgical robotics training. Within the virtual environment, surgeons can practice procedures and hone skills using robotics controls.
6 in 10 workers will require training before 2027, but only half of workers are seen to have access to adequate training opportunities today. The highest priority for skills training from 2023-2027 is analytical thinking, with the second priority is to promote creative thinking.— World Economic Forum, The Future of Jobs Report 2023
The transition from upskilling to comprehensive professional development represents a paradigm shift in how we approach learning and career growth. Embracing a holistic approach ensures that we are not only prepared for today’s challenges but are also equipped to navigate the complexities of the future professional landscape.
Although the transition is challenging, incorporating and embedding AI can be a powerful tool. Through AI-driven personalization, identification of skills gaps, continuous feedback, experiential learning enhancements and automation of administrative tasks, organizations can significantly improve their L&D efforts.
Note: The views expressed in this article are those of the individual and do not report the official position of the organization. The article uses lived experiences and research documents to formulate the thoughts mentioned above.















